In a world where science sometimes brings up strange or even unsettling discoveries, a recent finding is not only interesting but also quite fun.
This new discovery is a joyful one. Recent research shows that your hands, specifically your ring finger, could give clues about your personality. It turns out that the length of your ring finger may reveal important information about the amount of testosterone you were exposed to while in your mother’s womb. This makes it a surprising way to learn more about yourself.
At first, I was curious but unsure. When it comes to fingers, I usually think about palms, not lengths of digits. So I decided to take a look at my own hands and see if this test could really tell me something new.
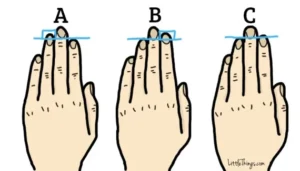
To my surprise, the results matched my personality quite well. When I compared my hand with the images provided, I saw that my ring finger was indeed longer than my index finger, which, according to the research, is a sign of an attractive and confident personality.
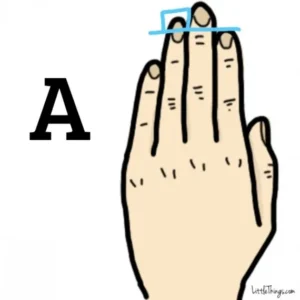
People like me, with a longer ring finger, are said to naturally attract attention and have a charming, confident vibe. One suggestion was to embrace my bold side because it could lead me to take exciting risks. The suggested careers, such as a soldier, a salesperson, or a CEO, fit surprisingly well with what I aim for in life.
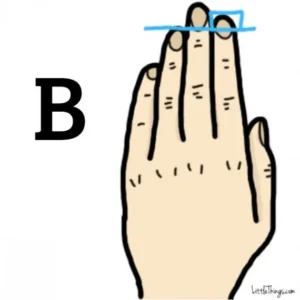
On the other hand, people whose index finger is longer than their ring finger (Hand “B”) are seen as natural leaders. These people are self-assured and take charge, helping others through tough times. Traits like being resourceful, calm, and confident were noted, which made sense to me. Career paths for them might include being a politician, author, or teacher—roles that involve leading and guiding others.
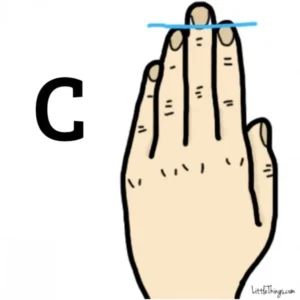
Lastly, there is Hand “C,” where the ring and index fingers are the same length. This suggests that the person is a good communicator and very balanced. If your fingers are even, you are likely someone others feel comfortable confiding in. You’re warm, a good listener, and you show a lot of compassion. Careers such as nursing, social work, or therapy are recommended for these individuals, which made me smile because those suggestions seemed surprisingly accurate.
In the end, this unusual personality test brought a mix of humor and deep thought. While the idea of fingers influencing our personality might seem hard to believe, the accuracy of the results and the career suggestions gave me something to think about.
If you want to see what your finger lengths say about you, why not give it a try? Take a look at your hands and see if your results match who you are. And don’t forget to share your findings with friends—maybe they’ll agree with their finger-based personality too!
Creating Unforgettable Memories: A Magical Wedding Surprise
Our wedding day will always be remembered as a significant event. There are innumerable incredible moments during the day that make us gasp and are truly moving. Occasionally, amid the flurry of feelings, unexpected events occur that cause our hearts to race.
Contents
Unlocking Dance’s Potential
Wedding dancing has long been a staple, bringing an extra dimension of happiness and celebration to the occasion. However, it has developed into something truly remarkable in recent decades. These days, surprising dancing performances that stun guests and maybe even the bride or groom are used to liven up celebrations.
A memorable incident of this kind happened at a Pennsylvania wedding. Four extraordinarily gifted young ladies enchanted the audience with an Irish dance. Under the direction of the Hooley School of Irish Dance, they skillfully put on a show that had everyone in stitches.

Enthralling Synchronization: An Unmatched Dance
Amidst the lively rhythms of “Shut up and Dance,” two elegant ladies skillfully entwined their feet in an impeccable demonstration of accuracy. These girls performed Irish dancing with grace and elegance. It’s an art form with an alluring appeal.
Before long, two more girls appeared on stage, dressed same. There was a tangible sense of excitement when five more dancers entered the stage and blended in flawlessly with the well-coordinated performance. They had outstanding timing and cooperation.
An Unexpected Reward
The audience was utterly enthralled, stunned by the incredible show that was playing out in front of them. The captivating dancers had everyone’s attention, but they had no idea what was in store for them. They had no idea that the stunning bride would appear with these young, gifted actors for a spectacular climax.

The bride’s seamless integration into the dancing routine resulted in an amazing moment of oneness. The joyful atmosphere of the occasion was evident from the room’s overflowing warmth and celebration.
To experience this incredible moment for yourself, click the video below, and get ready to be astounded by the unparalleled skill and surprise that transpired during Gretchen’s wedding reception:



Leave a Reply