
In recent years, the United States has faced a significant and deadly threat from the giant killer wasp, often referred to as the “murder hornet.” This invasive and highly destructive insect, known as the largest and most dangerous of its kind globally, first appeared in the country in 2019 and has since continued to spread fear and havoc.
The most recent sighting of this menacing creature occurred in Washington state in 2021. This discovery alarmed the region, as the “murder hornet” exhibited aggressive behavior, attacking anything that crossed its path. Measuring an imposing 4.4 centimeters in length, this insect was detected on August 11, just 3.2 kilometers from where it was first identified in December 2019, near Blaine, Washington, according to the Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA).
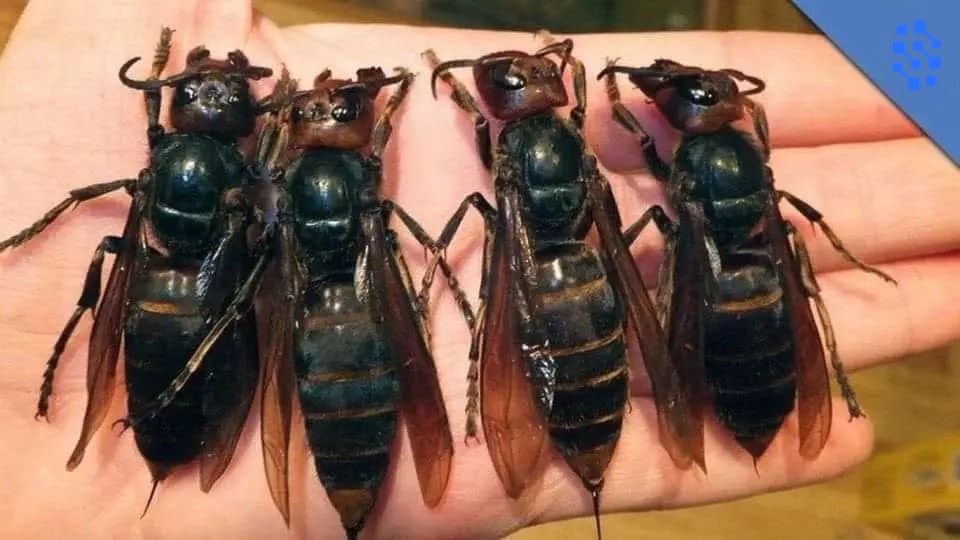

These hornets are notorious for their ability to decimate entire beehives. Their formidable mandibles allow them to kill and decapitate thousands of bees, taking over the hive and defending it as their own. They ruthlessly tear apart the brood to feed their offspring, leaving devastation in their wake. This is especially concerning given the critical role bees play in pollination and maintaining ecological balance.
Adding to the danger, the venom from a single sting of a “murder hornet” has the potential to kill a human. These hornets inject a significant amount of venom into their prey. While fatalities from a single sting are rare, the risk remains significant and alarming.
In response to this development, the WSDA is taking proactive measures to combat the threat. Live traps are being set up in the area, and entomologists plan to tag captured wasps to track them back to their nests. The proximity of this sighting to the US-Canada border has also prompted officials in that region to install additional traps to prevent the further spread of these deadly insects.
The emergence and spread of the giant killer wasp, or “murder hornet,” serves as a stark reminder of the threats nature can pose. With its potential to devastate bee populations and harm humans, efforts to monitor, control, and mitigate this invasive species are crucial to safeguarding both ecosystems and public safety. The ongoing efforts by state and regional authorities highlight the importance of swift and effective action in managing invasive species to protect the environment and human health.
10 Riddles Only Sharp Minds Can Solve
Are you ready for a mental workout? In this article, we’ve curated a collection of brain-bending riddles that will put logic and quick thinking to the test. Whether you’re an inquisitive mind or simply need a cerebral jolt, these brain-teasers are designed to challenge you. Can you crack them in just 7 seconds? Let’s find out.
Try to solve all the riddles and check the correct answers at the end of the article.
1.
A farmer in California owns a beautiful pear tree. The main trunk has 24 branches, each with 12 boughs, and each bough has 6 twigs.
<strong>Question: How many plums will the farmer be able to deliver?

2.
A wealthy family lived in a big circular house. After their parents left for a party, all the kids disappeared. The authorities questioned the butler, maid, and gardener. The butler claimed he was organizing the library, the maid said she was dusting the corners, and the gardener mentioned watering plants.
Question: Who’s lying?

3.
A woman in her hotel room hears a knock. Then a man enters her room and she screams. Upon calling security, he claims he mistook her room for his.
Question: Was the man lying?

4.
Grandpa went for a walk in the rain without an umbrella or hat. His clothes got soaked, but his head remained dry.
Question: How could this happen?

5.
Question: Can you solve it?
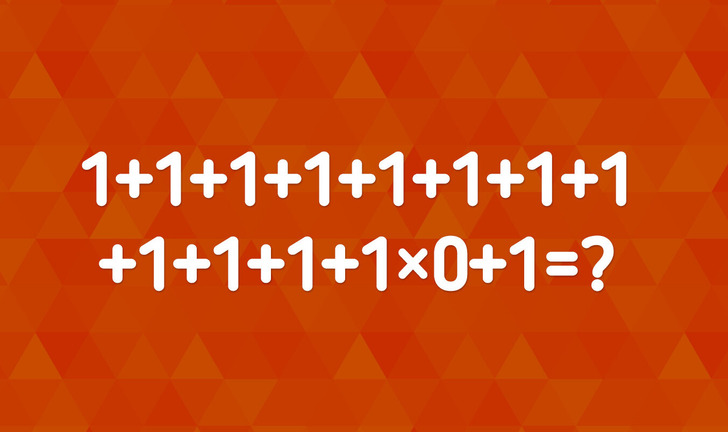
6.
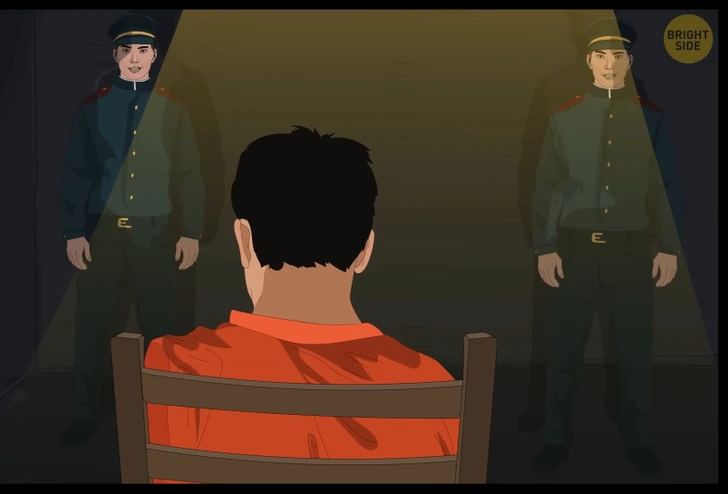
A prisoner is in a cell with two doors—one leads to freedom, and the other leads to certain death. There are two guards—one always tells the truth, and the other always lies. You don’t know which guard is which.
Question: What one question can you ask to determine the correct door?

7.
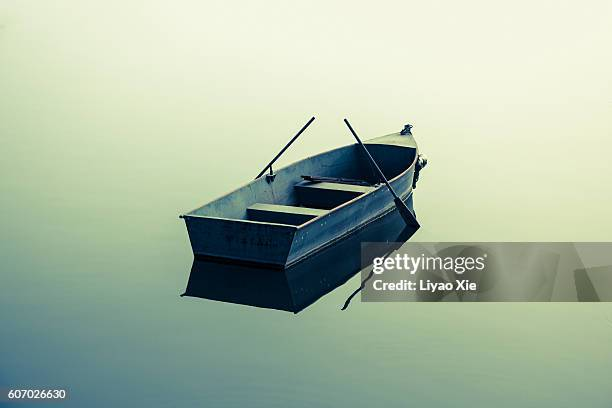
You see a boat filled with people. It has not sunk, but when you look again, you don’t see a single person on the boat.
Question: Why?

8.
I am not a living creature, but I can move and grow. My size is determined by how you use me. I can be a refuge or a prison, depending on how I am made. Some people fear me, while others feel comfort within me. I am made of many different parts, but I am always whole.
Question: What am I?
9.
I am seen in the water, but I never get wet. I am always changing, yet I always remain the same. I can appear in front of you, but if you reach for me, you won’t be able to touch me. I exist because of light, but I have no light of my own.
Question: What is it?

10.
Question: Which option below is the closest time to midnight?

Answers:
1.
None, he has a pear tree.
2.
The maid. The circular house had no corners that she could clean.
3.
Yes, the man was lying. If it was his room, he’d have tried to open the door, not knock first.
4.
Grandpa’s head remained dry because he was bald.
5.
According to the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS), multiplication comes before addition. So, we first solve the multiplication part. Then do the addition. The final answer is 12.
6.
Ask either guard, “If I were to ask the other guard which door leads to freedom, what would he say?” Then choose the opposite door.
7.
All the people were married.
8.
A story.
9.
Reflection.
10.
The time closest to midnight is 12:04 am.
Up for your next dose of brain riddles?



Leave a Reply