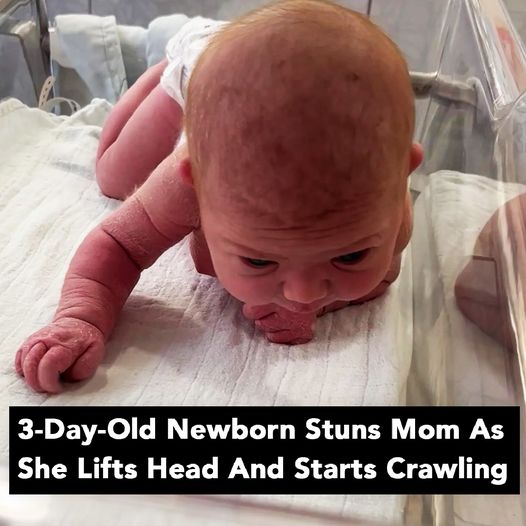
Three weeks past her due date, Nyilah Daise Tzabari made her grand entrance into the world with an eagerness to make up for lost time. At just three days old, she stunned her parents by lifting her head and crawling across her hospital cot.
Nyilah’s extraordinary strength left her first-time parents, Samantha Mitchell and Ofer Tzabari, in awe. Still in the hospital, the couple managed to capture the moment on video, showing their daughter doing things typically seen in much older babies.
“The video was taken when Nyilah wasn’t even a full three days old—she was only two and a half days old,” Samantha shared. A 34-year-old mother from White Oak, PA, Samantha was amazed, saying that despite her two decades of experience with children, she had never seen anything like it. “I’ve never had a newborn like this,” she added.
In the viral TikTok video, which has now garnered over 57.5 million views, baby Nyilah uses her tiny arms to prop herself up and crawl. In the background, you can hear Samantha’s mother exclaiming in disbelief, while Samantha herself is equally astonished, saying, “Oh my gosh. Mom! She’s crawling! How does that even move?”
Nyilah was born on February 27, 2023, weighing 7 lbs 6 oz. Samantha, who initially recorded the video to show family and friends, said, “If I didn’t get it on film, no one would have believed me, not even my fiancé, Ofer.” The video captures the exact moment Samantha witnessed her baby crawl for the first time, leaving her in complete shock.
Fans on TikTok were just as amazed, with many joking that “these new babies are different—they come out crawling and walking at one month old.” Others chimed in with lighthearted comments, saying, “Rumor has it she left on a plane the next day to live her life.”
According to Healthline, most babies start to crawl between six to 12 months, but Nyilah is clearly on a fast track. In fact, her quick development has continued since that viral moment. At 18 days old, she was already rolling from her belly to her back. By one month, she was smiling at her mom, and by two months, she was rolling from her back to her belly. At three months, she was even showing off her strength by playfully punching her mom in the face during a video.
Nyilah’s rapid growth hasn’t stopped there. She is already standing with support, and Samantha is confident that walking is just around the corner. “She puts so much weight on her legs and refuses to buckle her knees,” Samantha shared, adding that Nyilah no longer even needs her head and neck supported.
“She’s a very alert baby, and her strength has surprised us from day one,” Samantha said. At seven weeks, Nyilah began babbling and mimicking words spoken by her parents, even trying to say, “I love you.” She loves making noises to get a reaction, showcasing her playful and clever personality.
Nyilah is not just strong but also incredibly happy. “She smiles and laughs all the time,” Samantha said. “The second you smile at her, she lights up and smiles right back.”
For Samantha and Ofer, their daughter’s actions have been a pleasant surprise. “I thought this was normal for newborns, but it turns out Nyilah’s behavior is far from typical,” Samantha explained.
As Nyilah continues to grow and amaze, her family is preparing for even more milestones. With her rapid development, the future is sure to be filled with excitement. Samantha and Ofer’s “super baby” is already taking the world by storm, and we can’t wait to see what she does next! Congratulations to the happy family!
My In-Laws Refused to Come for Thanksgiving but Sent Us a ‘Gift’ – When My Husband Opened It, He Screamed, ‘We Have to Drive to Their Home Now!’

My husband and I had an incredible bond with his parents, to the point of seeing them as close friends. But after we discovered we were pregnant, my in-laws started pulling away before we could share the good news, only for us to find out they had been hiding something shocking!
My husband, Ethan, and I have always had an amazing relationship with his parents, Linda and Rick. But when they started acting distant and weird, we ended up driving unannounced to their home to confront them!

An upset couple driving | Source: Midjourney
See, my 45-year-old mother-in-law (MIL) and 47-year-old father-in-law (FIL) are the kind of in-laws everyone dreams about. They’re young enough to be fun and adventurous but still undeniably “parent-y” when it counts. Linda had Ethan when she was just seventeen, and Rick wasn’t much older.
They’re an inspirational couple who have the perfect balance of energy and wisdom and are more like friends than your typical in-laws. Lately, though, they’ve been acting… different.

An older couple | Source: Midjourney
It started a few months ago when Ethan’s father began dodging his calls with bizarre excuses, like saying he was busy “working on the attic” when they lived in a single-story house or fixing the porch when they didn’t have one.
The calls were always strained and abruptly cut off from my FIL’s end. Linda, who typically bombarded me with memes and baking recipes, suddenly went silent. When I did reach out, her responses were curt, emoji-laden replies that made no sense.

An older woman texting | Source: Midjourney
Once, when I asked if they’d watched a particular movie, she replied by sending me a spaghetti emoji! Ethan brushed it off as her being “quirky” though I couldn’t shake the feeling that something was wrong.
But the first obvious red flag had to do with their guest room, which Rick was quite protective about. We visited them last month and for the first time, the room’s door was locked! When Ethan jokingly threatened to pick the lock, Linda’s sharp “Don’t you dare!” left us both stunned.

An upset older woman shouting | Source: Midjourney
Awkward is an understatement for how the rest of that visit went! The warmth and humor they usually radiated had been replaced by a tension we didn’t understand.
The second red flag had to do with the Thanksgiving holiday, which we hoped would bring us back together. We’d been planning to host the holiday for weeks and were eager to share some life-changing news with them: we were expecting our first child! We even bought a tiny, adorable onesie that said “Grandma & Grandpa’s Little Turkey” to make the announcement extra special!

A baby’s onesie | Source: Midjourney
But a week before the holiday, Linda called and said they wouldn’t make it. “We have something going on,” she said vaguely.
Ethan pressed for details, but all she gave him was a frustrated, “You wouldn’t understand.”
My husband was furious. “Something’s going on with them,” he said, pacing the kitchen that evening. “They’re hiding something. Why can’t they just talk to us?”
He even threatened to drive over and confront them, but I convinced him to let it go. I figured everyone deserved their privacy. But their absence hurt more than I expected.

An upset man | Source: Midjourney
Thanksgiving morning came, and instead of a bustling house filled with family, it was just Ethan and me because I wasn’t close with my parents or my side of the family. We made the best of it, but the elephant in the room, his parents’ unexplained absence, was impossible to ignore.
The holiday felt lonely without them there, but around 3 p.m., the doorbell rang. A delivery man presented us with a medium-sized package addressed to Ethan.

A man holding a box | Source: Midjourney
After signing for the “gift,” we noticed a note taped to the top that read: “We’re so sorry we couldn’t be there. Please open this together. Love, Mom & Dad.”
My husband carried the box inside, and I set up my phone to record our reaction, thinking it might be a heartfelt gesture, like a photo album or one of Linda’s famous quilts.
Ethan tore into the package, pulling out a plain cardboard box. Inside, nestled among layers of tissue paper, was something I couldn’t see. It took him a moment to register what he was looking at. Then his face drained of color, and he let out a guttural scream!
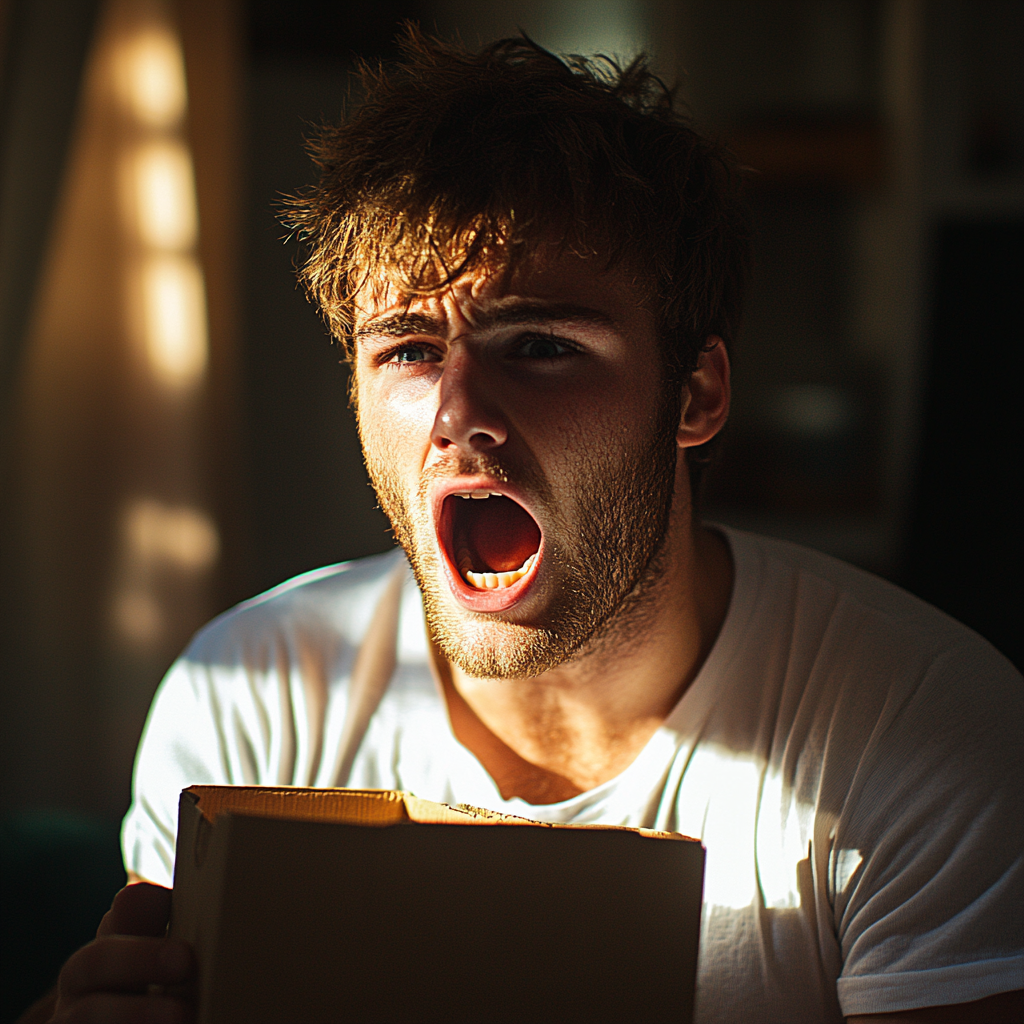

A man screaming | Source: Midjourney
“We have to go. Now!”
“What? What’s wrong?” I asked, my heart racing.
Ethan didn’t answer. He grabbed his keys, slipped on his sneakers, and motioned for me to follow. “Get in the car. We have to drive to my parents’ house now!”
“Ethan, you’re scaring me. What was in the box?”
“You wouldn’t believe me if I told you. We need to hear this from my parents,” he muttered as he buckled his seatbelt. His hands gripped the steering wheel so tightly that his knuckles turned white!
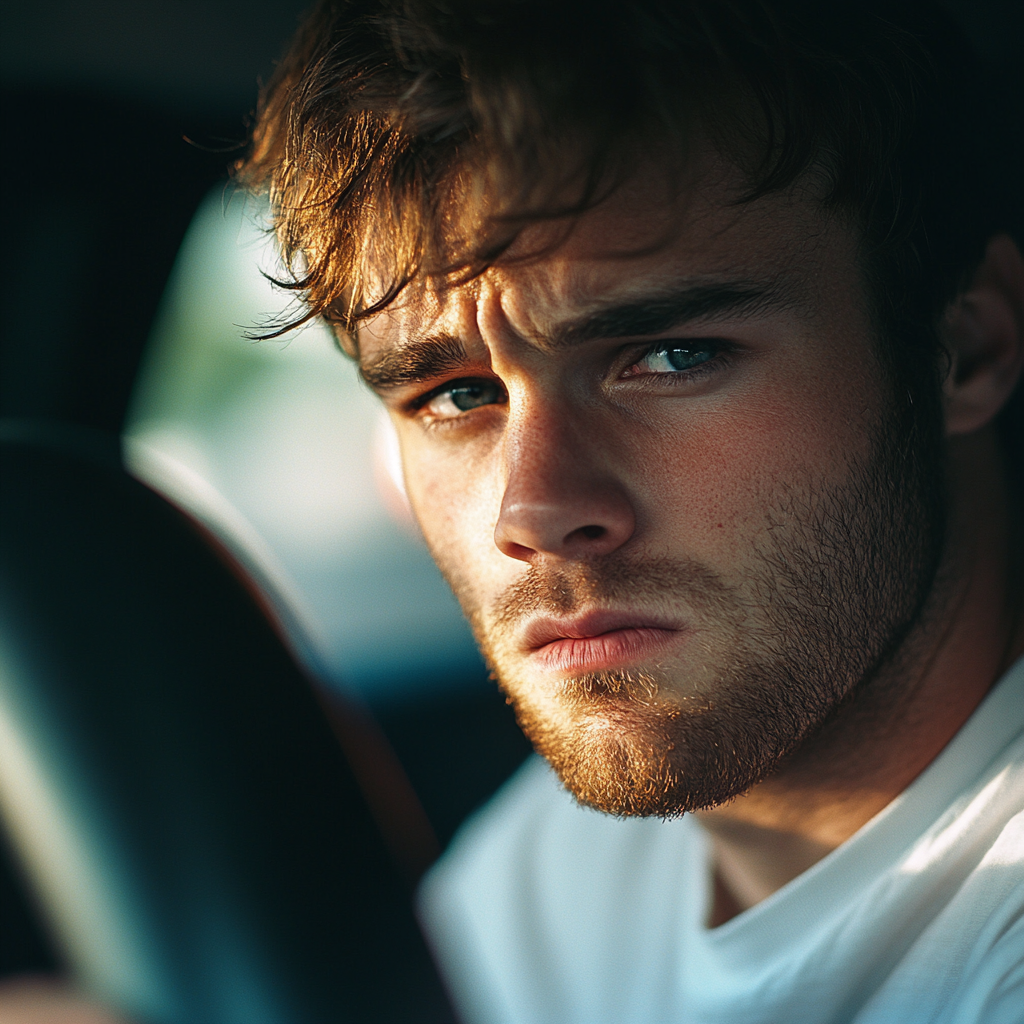

An upset man driving | Source: Midjourney
The five-hour drive to his parents’ house was agonizing. Ethan wouldn’t say a word, leaving my imagination to run wild! Was someone sick? Hurt? Was this their way of calling for help? Or did they have a fallout they didn’t mention? Or maybe they were in danger?!
By the time we pulled into their driveway, my nerves were shot! I was partially convinced that the FBI would be waiting inside! I was about to knock when Ethan threw the door open! Linda and Rick, startled by our sudden arrival, jumped to their feet!
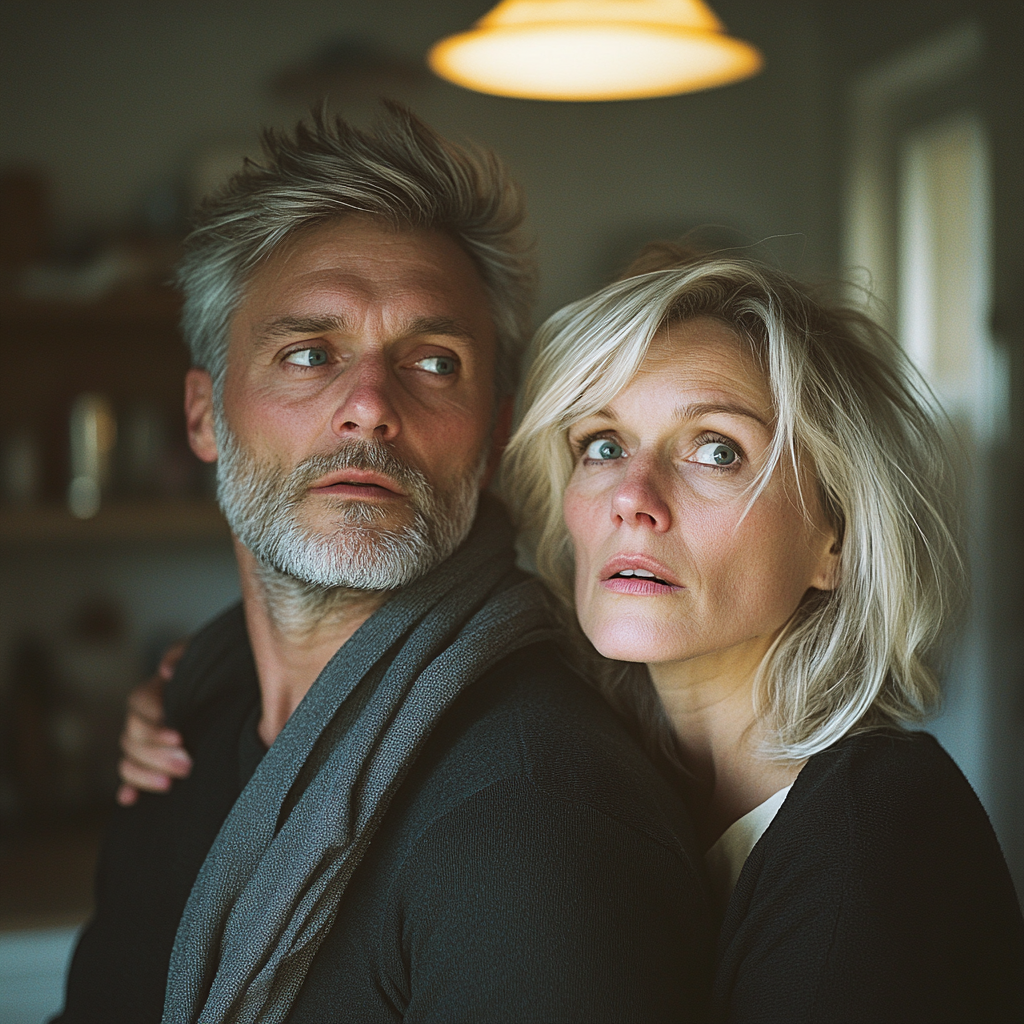

A shocked older couple | Source: Midjourney
Ethan got straight to the point, holding up the box and taking out a pregnancy test. “What. Is. This?”
My FIL’s face turned ashen, and Linda’s cheeks flushed deep red. She looked at me, then back at Ethan, and finally stammered out, “I—I was going to call.”
“Call?!” Ethan’s voice was incredulous with hurt. “You thought sending this was a better idea than just telling us?!”
My MIL wrung her hands nervously. “I didn’t know how to say it.”
“Say what?” I interjected, my voice trembling.
Linda took a deep breath, her eyes welling with tears. “I’m pregnant.”
Silence. Complete, deafening silence.
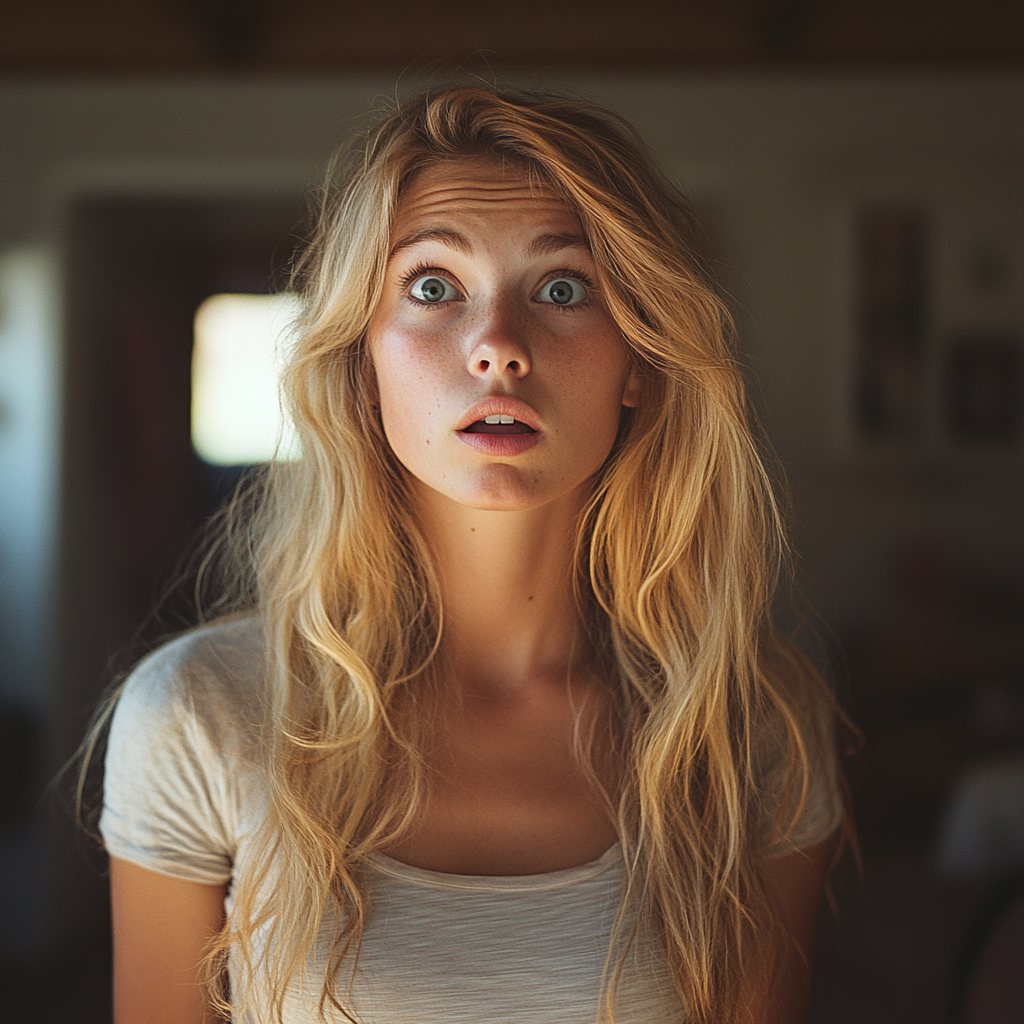

A shocked woman | Source: Midjourney
I blinked at her, sure I’d misheard. “You’re…what?”
Rick cleared his throat, his voice thick with emotion.
“It’s true. We didn’t think it was possible. I mean, I had a vasectomy years ago.”
He laughed nervously. “Guess it wasn’t as foolproof as we thought.”
“We were so overwhelmed by this news and trying to figure out how to break it to you that we panicked and chose to avoid you instead,” Rick explained.

An older man | Source: Midjourney
“We skipped Thanksgiving because we hadn’t mentioned the pregnancy beforehand and didn’t want to suddenly arrive with a pregnant belly! We thought the test was the way to tell you the news,” Linda continued.
The cryptic messages. The avoidance. Suddenly, it all made sense! At their age, a baby wasn’t just unexpected, it was unimaginable!
“You couldn’t have just told us?” Ethan asked, his voice softer now. “We would’ve understood.”
Linda’s face crumpled.

A sad older woman | Source: Midjourney
“We didn’t know how you’d react. I mean, this is insane, right? We’re about to be new parents again! How could we explain that?”
My husband’s expression softened, and he let out a shaky laugh.
“Yeah, it’s insane that I’m going to be a big brother to someone. But it’s not something you needed to hide.”
Finally, my husband and I looked at each other and started laughing before I reached into my bag, pulling out the onesie we’d planned to give them. Luckily, I hadn’t taken it out of my bag since we bought it, so I handed it to Linda.
“Congratulations, Grandma and Grandpa. You guys are going to be grandparents and parents at the same time!”

A woman handing over a onesie to someone | Source: Midjourney
My MIL stared at the onesie for a moment before bursting into tears. “You’re pregnant?”
I nodded, tears springing to my own eyes. “Looks like this family’s about to get a lot bigger!”
Rick enveloped Ethan in a bear hug, while Linda pulled me into hers! The weight of the past few months seemed to lift at that moment, replaced by something lighter: joy, relief, and maybe even a little humor at the absurdity of it all.

Two men hugging | Source: Midjourney
The rest of the night was a blur of laughter and celebration. Linda showed us the guest room, which they converted into a nursery filled with baby clothes and a crib. That’s why they kept it locked.
Rick pulled out a bottle of sparkling cider, and we toasted to the wildest Thanksgiving any of us had ever had! Ethan and I promised we’d work with them to help navigate this next chapter, and they swore to stop keeping secrets from us. As we sat around the table, pie crumbs scattered across our plates, Linda reached for my hand.

A couple having Thanksgiving dinner | Source: Midjourney
“I’m sorry we’ve been so distant. I was so scared of what you’d think, but I should’ve trusted you,” she said.
I squeezed her hand. “We’re family. That’s what we’re here for.”
Ethan leaned back in his chair, a wide grin on his face. “So, Mom, what do you think about a joint baby shower?”
Linda laughed, wiping away the last of her tears. “Only if you let me bring the spaghetti emoji cake!”
We all erupted into laughter, the kind that leaves your cheeks sore and your heart full. Thanksgiving hadn’t gone as planned, but in its own chaotic way, it had brought us closer than ever.

Two couples enjoying a meal | Source: Midjourney
If you enjoyed that story, then you’ll love this one about a couple who were thrilled when they discovered they were pregnant, only for the woman’s MIL to steal their thunder by announcing the news to the family. Tired of being bullied, the daughter-in-law sought revenge to teach her a lesson.
This work is inspired by real events and people, but it has been fictionalized for creative purposes. Names, characters, and details have been changed to protect privacy and enhance the narrative. Any resemblance to actual persons, living or dead, or actual events is purely coincidental and not intended by the author.
The author and publisher make no claims to the accuracy of events or the portrayal of characters and are not liable for any misinterpretation. This story is provided “as is,” and any opinions expressed are those of the characters and do not reflect the views of the author or publisher.



Leave a Reply