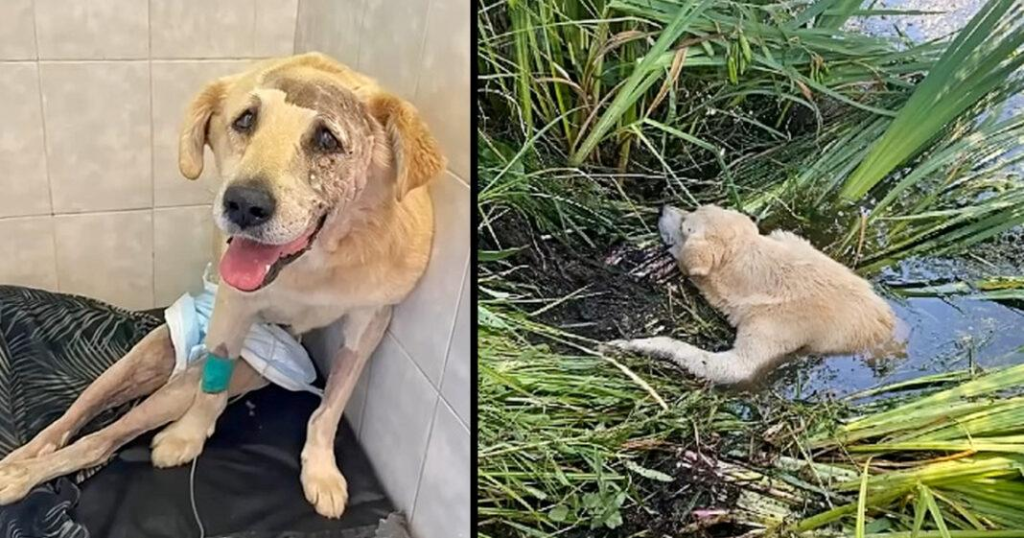

Broddick’s story was heartbreaking and moving to the bone. Some dogs followed the unfortunate dog, and while escaping, he slipped into a river and became caught in it.
He had several bruises and swellings on his neck, head, ears, and cheeks. His left eye was injured and only partly closed. There were no words to convey how desperate he appeared at that moment.
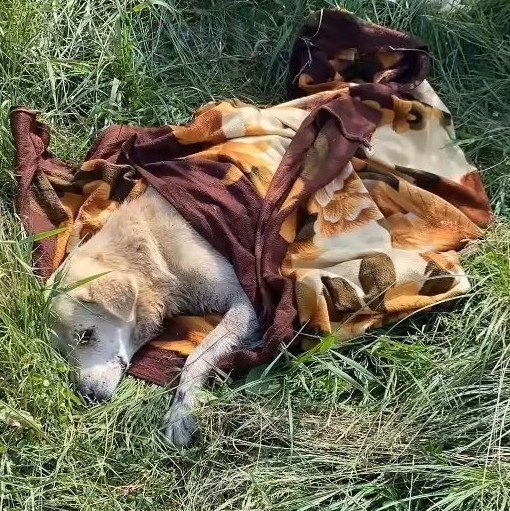

A nice Samaritan arrived around six o’clock in the morning and brought him to the emergency vet. Brodick’s herniated discs were causing him a lot of difficulties and pain, so the doctor started treating him for spinal block.
Brodick was a bright and understanding dog, but he was unlucky in life. Surely, the days of pain will come to an end.

His scratches and bites on his body had nearly totally healed, and his skin had smoothed out. He was taken off the wing and guided with a support belt. He was eating properly, but his weight had dropped.
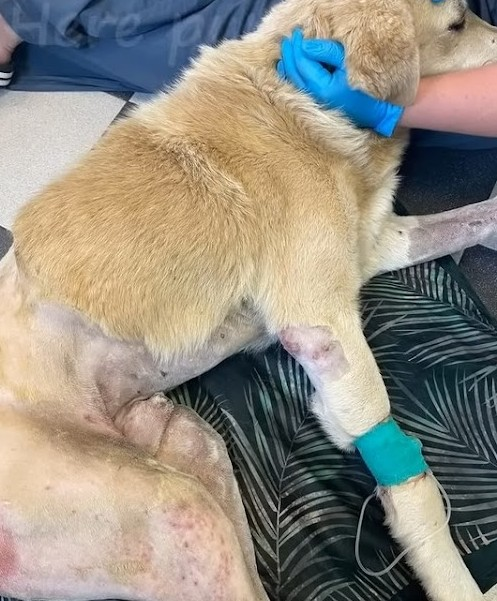
Brodick was able to breathe fresh air when the wheelchair was significantly changed. The bad news is that the lining is flowering and the parallel gland may have decayed.

Brodick’s basic health remained unchanged; he was eating, drinking, and defecating mainly formally. Throughout the night, there were violent seizures. The cause was necrosis, which was spreading rapidly. Despite regular therapy with chymotrypsin, it can spread throughout the body.
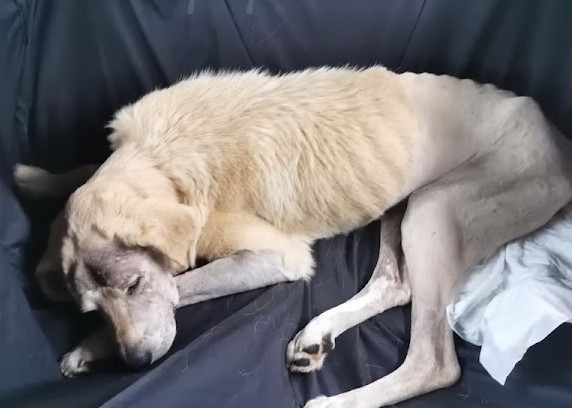

Brodick also had a huge tumor in his spine that had developed into soft tissue; unfortunately, this tumor is cancerous. Sepsis had begun, according to blood tests. Stronger pain medicines barely worked for a few hours.
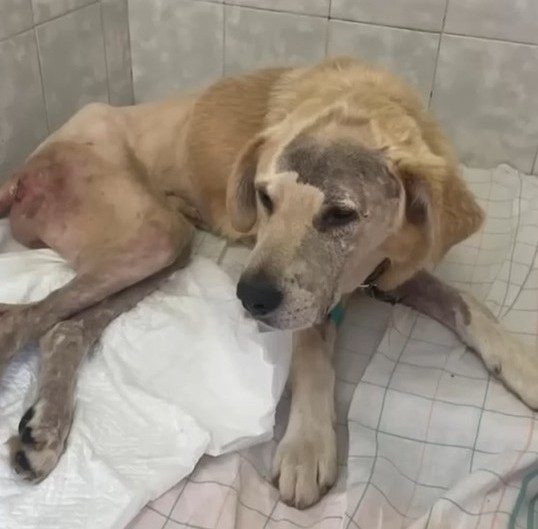
Vets chose to let Brodick go where he was confident there would be no more pain after several days of thought.
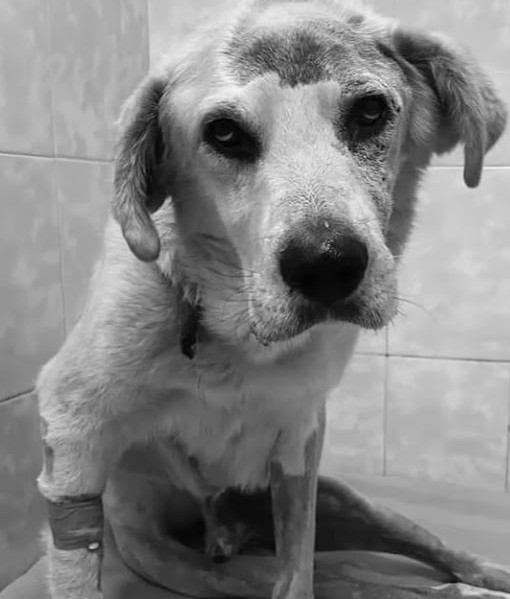

“Soft clouds to you in paradise, our sweet Brodick.”
Dog rescued after getting its head stuck in wheel rim
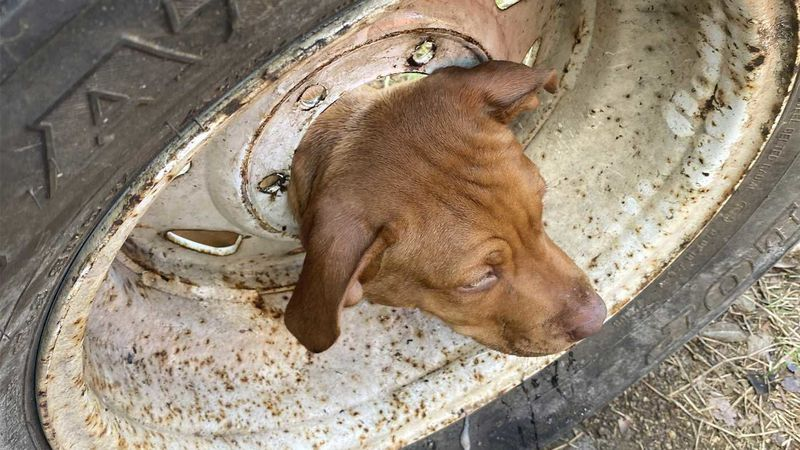

A dog has been rescued from a tight spot by Queensland firefighters armed with a bottle of olive oil and a lot of patience.
The puppy, named Bonnie, stuck its head through the middle of a wheel rim but couldn’t pull itself back out.
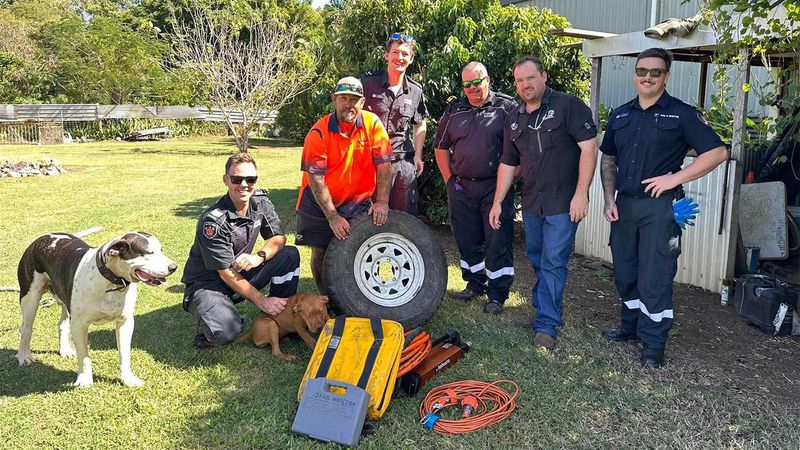
It was up to the firefighters at Mareeba Fire and Rescue to figure out a solution to the sticky situation.
“Crews used lots of olive oil and patience to assist in the extrication,” Queensland Fire and Emergency Services said in a Facebook post.
“We hear she’s recovering well.”
Mareeba is a rural town in Far North Queensland, inland from Cairns.




Leave a Reply