Dry, flaky skin can result from various factors, including genetics and aging, which naturally predispose some individuals to this condition. If left untreated, dry skin can crack, increasing the risk of infections. Fortunately, there are many remedies and lifestyle adjustments to help restore and maintain hydrated, healthy skin.
Shower Smarter

Frequent washing can strip the skin of its natural oils, making it more prone to dryness. To lock in moisture and protect your skin:
- Use lukewarm water: Avoid hot water, which can exacerbate dryness.
- Pat dry gently: Use a towel to pat your skin dry instead of rubbing.
- Moisturize immediately: Apply moisturizer while your skin is still damp to seal in hydration.
- Shave wisely: Always use shaving gel and a sharp razor to reduce irritation.
Combat Winter Dryness
Winter weather is particularly harsh on the skin due to cold air and frequent handwashing. To minimize its effects:
- Wear gloves: Protect your hands outdoors and while performing tasks like dishwashing.
- Use a humidifier: Adding moisture to indoor air can prevent dryness, as recommended by dermatologists.

Natural Remedies for Dry Skin
1. Olive Oil
Extra-virgin olive oil is rich in vitamin E and antioxidants, making it effective for repairing dry skin. Apply sparingly to dry areas such as elbows or mix it with a face mask for added hydration. Avoid overuse, as it may weaken the skin barrier.
2. Oatmeal Baths
Adding a cup of oatmeal to warm bathwater can hydrate and soothe irritated skin. This remedy also alleviates itchiness and discomfort caused by dryness.
3. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil works as a natural moisturizing cream. Apply it to chapped hands, feet, or heels before bed for intense hydration. For better results, wear gloves or socks after application.

4. Milk Compress
Milk contains lactic acid and anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe and gently exfoliate dry skin. Soak a clean washcloth in cool milk and apply it to affected areas for 5–10 minutes. Avoid this method on cracked skin.
5. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is known for reducing redness, irritation, and dryness. Its mucopolysaccharides, similar to hyaluronic acid, help retain moisture. Perform a patch test before applying it to larger areas of skin.
6. Honey
Honey is a natural humectant with healing and anti-inflammatory properties. Use it as a spot treatment for rough patches or include it in homemade face masks. Consult a dermatologist before using honey to treat specific skin conditions.
7. Petroleum Jelly
Products like Vaseline or Aquaphor create a protective barrier to lock in moisture and prevent chafing. Petroleum jelly is suitable for sensitive areas like eyelids and lips but should be avoided on acne-prone areas.

Choosing the Right Products
When selecting skincare products, opt for ointments or creams instead of lotions for better hydration. Look for these key features:
- Fragrance-Free: Choose products labeled as “fragrance-free” rather than “unscented,” which may still contain irritants.
- Hydrating Ingredients: Seek out components like ceramides, glycerin, and hyaluronic acid for effective moisture retention.

When to Consult a Doctor
If dryness persists despite home remedies, it may signal an underlying skin condition. Consult a dermatologist for professional care or prescription treatments tailored to your needs.
By following these tips and incorporating natural remedies, you can effectively manage dry, flaky skin and maintain a healthy, glowing complexion.
Why don’t airplanes fly in a straight line to save fuel?
Have you ever looked at a flight path on a map and wondered why airplanes take curved routes instead of flying in a straight line? Wouldn’t flying in a direct line be more fuel-efficient and faster? At first glance, it seems logical that a shorter distance would result in less fuel consumption, but in reality, aviation is far more complex.
Several factors determine flight paths, including the Earth’s shape, jet streams, weather conditions, and air traffic regulations. Let’s break down why airplanes rarely fly in a straight line and how their curved paths actually make flights more efficient.
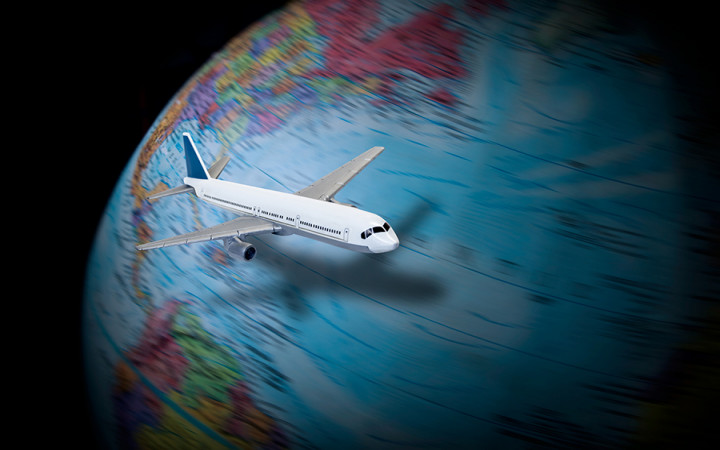
The Earth’s Shape and the Great Circle Route

One of the biggest reasons airplanes don’t fly in a straight line is the Earth’s curvature. While we often view flight maps as flat, the Earth is a sphere, and the shortest path between two points is actually an arc called the Great Circle Route.
If you take a globe and use a string to connect two distant locations, you’ll notice that the shortest route often curves rather than follows a straight path. This is why flights from New York to Tokyo pass over the Arctic region rather than flying directly west across the Pacific Ocean.
Using the Great Circle Route helps planes save both time and fuel, even though it appears curved on a flat map.
Jet Streams and Weather Conditions Impact Flight Paths
Another key factor affecting airplane routes is jet streams—high-altitude wind currents that move at speeds of up to 200 mph (320 km/h). Pilots strategically plan routes to take advantage of these strong winds when possible.
Video : Why Airplanes Don’t Fly Straight
Flying with jet streams allows an airplane to get an extra push, helping it move faster while burning less fuel. Flying against a jet stream can slow down the plane significantly, increasing fuel consumption. Pilots often adjust routes to avoid strong headwinds, even if it means flying a longer distance.
Additionally, storms, turbulence, and severe weather conditions also play a role in determining flight paths. Airplanes may adjust mid-flight to bypass dangerous weather zones, thunderstorms, or areas with extreme turbulence.
Air Traffic Control and Flight Regulations
Air traffic isn’t a free-for-all where planes can just fly wherever they want. There are strict regulations set by aviation authorities and air traffic control (ATC) that dictate flight routes.
Some of these rules include restricted airspace, where certain areas, such as military zones, national security locations, and political zones, prohibit commercial flights from entering. Predefined flight corridors exist to avoid mid-air collisions, ensuring flights follow established air traffic lanes. Major airports handle hundreds of flights daily, so ATC ensures safe and efficient arrivals and departures.
Due to these regulations, airplanes cannot always take the most direct path and must follow designated routes instead.
Avoiding Air Turbulence for Passenger Comfort
Turbulence can make a flight uncomfortable, and pilots actively adjust routes to minimize rough air conditions. There are different types of turbulence, including thermal turbulence caused by warm air rising from the ground. Flying at higher altitudes helps avoid this.

Mechanical turbulence happens near mountains and rough terrains where wind patterns shift unpredictably. Clear-Air Turbulence (CAT) is sudden, strong air currents in high altitudes that are difficult to predict.
To ensure a smoother ride for passengers, pilots may deviate from the shortest path to avoid these turbulent areas.
Why Do Airplanes Sometimes Ascend Before Landing?
If you’ve ever been on a flight where the plane suddenly climbs just before landing, you might have felt a bit concerned. This maneuver is known as a go-around and is actually a common and safe aviation practice.
Some reasons why pilots perform a go-around include runway clearance issues. If another plane hasn’t cleared the runway in time, pilots must abort the landing and circle back. Poor weather conditions, such as poor visibility, strong crosswinds, or sudden gusts, can make a landing unsafe. If a plane is too fast, too high, or not properly aligned with the runway, the pilot will ascend and try again for a safer landing.
Go-arounds are standard procedures in aviation and ensure passenger safety above all else.
The World’s Longest Non-Stop Flight
While most flights follow curved paths, some routes push the limits of non-stop travel. The longest direct commercial flight in the world is from Singapore to Newark, New Jersey, USA.
This flight covers a distance of 10,400 miles (16,700 km) and takes approximately 18 hours and 45 minutes. It follows a carefully optimized path to balance fuel efficiency, wind conditions, and passenger comfort.
Video : Does Earth’s Rotation affect the Airplanes Speed & Flight Time
What Happens If a Plane Suddenly Loses Cabin Pressure?
A sudden drop in cabin pressure is often portrayed as a dramatic event in movies, but in reality, pilots are well-trained to handle it calmly.
When this happens, oxygen masks automatically deploy, and passengers should put them on immediately and breathe normally. The plane will descend to a safe altitude where oxygen levels are sufficient for breathing. The flight crew will assess the situation and communicate with passengers.
Losing cabin pressure doesn’t mean the plane will crash—pilots follow strict safety protocols to handle such incidents efficiently.
Final Thoughts: Why Curved Flight Paths Are More Efficient
While it may seem counterintuitive, airplanes take curved routes instead of straight lines to optimize flight efficiency, fuel usage, and passenger safety. Factors such as the Earth’s shape, jet streams, air traffic control, and weather conditions all play a crucial role in determining flight paths.
So next time you’re on a plane and see the route map displaying a curved flight path, remember there’s a lot of science and planning behind it to ensure you reach your destination as safely and efficiently as possible.



Leave a Reply