
Demi Moore and Bruce Willis are often regarded as the most amicable ex-couples in Hollywood. The pair, who have been married for 11 years and have three daughters, Rumer, 34, Scout, 31, and Tallulah, 28, have become even closer since Bruce’s aphasia diagnosis.
The degenerative illness diminishes a person’s ability to comprehend and communicate in the language.
Bruce Heming, the actor in Die Hard, said earlier this year that he would retire from acting due to sickness, along with his children and his 13-year wife, Emma Heming.
According to a source, Demi has kept in touch with Bruce and Emma regularly. She will call the phone if she is not at his side just so Bruce can hear her voice. She is doing everything she can to be with him.
The entire family is rallying behind the 67-year-old celebrity. According to the insider, they know he will not be present indefinitely. As a result, they appreciate every minute.
Demi and Bruce’s extended family, including his two kids with Emma, ages 10 and 8, frequently vacations in Idaho.
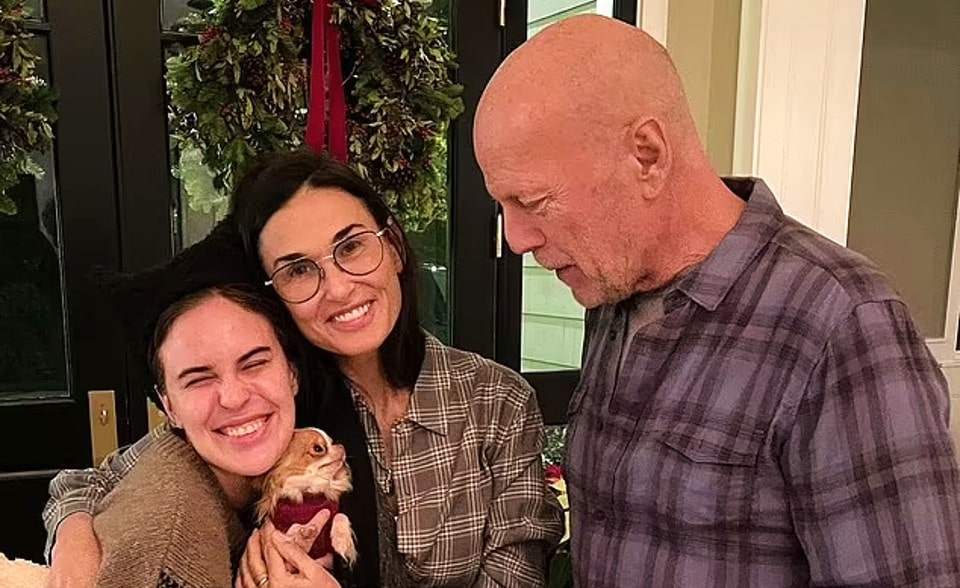
“It was always a special occasion,” stated the insider. The favorite family traditions, such as pajama parties and game nights, survived.
Demi and Emma’s friendship has become stronger as they both struggle with Bruce’s decline. His wife is now serving as a middleman between their ex-partners.
“Bruce can’t say much, and it doesn’t appear like he understands much of what others say,” an insider said. Emma has been his major spokesman and communication channel.

Despite his worsening condition, his loved ones are doing everything they can to keep him alive, especially with the holiday season approaching.
“There are occasions when they catch glimmers of the old Bruce,” the insider claimed, “but they are few and far between.” They are heartbroken because he appears to be sliding further away.
They are all eager to spend the holidays with their adored father. “The girls can’t imagine Christmas without Bruce,” a source alleged. The older girls miss the old Bruce, who used to mock them about their boyfriends and give them advice. “It’s been awful to see him deteriorate.”
“All they can do is tell him they love him and hope for a holiday miracle with Christmas right around the way,” the insider stated.
Trypophobia
Trypophobia is a relatively lesser-known psychological phenomenon characterized by an intense aversion or fear of clustered patterns of small holes, bumps, or irregular shapes. While not officially recognized as a distinct mental disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), trypophobia has gained attention in recent years due to its prevalence and the emotional distress it can cause in individuals who experience it.
People with trypophobia often react strongly to images or objects that exhibit repetitive and closely packed small holes, such as lotus seed pods, honeycombs, or certain types of coral. The term “trypophobia” itself is derived from the Greek words “trypo,” meaning “hole,” and “phobia,” indicating an irrational fear. It’s important to note that trypophobia is not limited to specific shapes or textures; it encompasses a wide range of stimuli, and triggers can vary from person to person.
The fear response associated with trypophobia may manifest as feelings of discomfort, anxiety, nausea, or even panic attacks. Some individuals may go to great lengths to avoid situations or objects that could trigger their trypophobia, impacting their daily lives. While the exact cause of trypophobia remains unclear, researchers speculate that it may be linked to evolutionary factors, as some dangerous animals and plants exhibit similar patterns in nature.
Social media and the internet have played a significant role in popularizing trypophobia, with numerous online communities sharing images and discussions related to this phenomenon. The widespread dissemination of trypophobic triggers has led to increased awareness and recognition of this condition. However, it’s crucial to approach the topic with sensitivity, as exposure to triggering images can genuinely distress individuals who experience trypophobia.
Despite its prevalence, trypophobia remains an area of ongoing research, and professionals in psychology and psychiatry continue to explore its origins, manifestations, and potential treatments. Understanding trypophobia can contribute to more compassionate and informed discussions about mental health, promoting empathy and support for those who grapple with this unique fear.



Leave a Reply