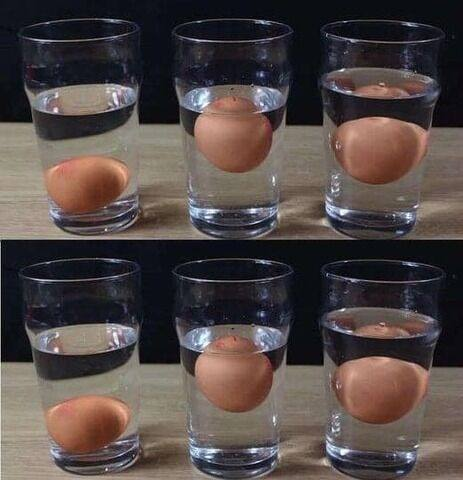
Uncertain about egg freshness when cooking? Here are some simple tips to assess freshness and cut down on egg-related food waste. Supermarket eggs are labeled with a use-by date, and in France, eggs can’t be sold seven days before this date. Eggs from a henhouse stay fresh for up to 28 days after being laid.
Refrigerated eggs, even with intact shells, are safe for consumption for up to one month past the use-by date, equating to 58 days post-laying. Proper storage practices help maintain freshness and minimize waste. Expired eggs may emit an off-putting odor. A bad smell indicates loss of vitamins and an altered taste. If it smells normal, consider using it quickly, such as in an omelet.
Inspecting the shell and egg color is essential for detecting spoilage. Powdery or cracked shells may suggest the presence of mold. Unusual colors in the egg white or yolk, like blue or green, are indicators of spoilage. By adopting proper storage techniques and remaining vigilant, you can prevent egg waste while ensuring your meals remain fresh and safe.
Remember, proper storage in the refrigerator is crucial for maintaining egg freshness and reducing health risks. By adhering to these simple guidelines, you can confidently use eggs in your recipes, knowing they are safe and fresh.
No one shows up for 6-year-old’s birthday party – then mom shares picture and the community steps up
For one youngster named Teddy, it was supposed to be the finest day of his life, but instead it was a terrible experience. His parents wanted to take him to Lego Land or Disney World for his sixth birthday, but he preferred to celebrate with his pals.
About two weeks prior to the big day, Teddy’s mother reserved a table at Peter Piper Pizza and handed 32 invitations to Teddy’s teacher, asking her to give one to each student in the class. More over half of the parents of the children stated they would bring the kids to the celebration.
Teddy’s mother Sia ordered a large pizza and made gift bags for her son’s buddies for his birthday. Even though everyone was expecting to have a blast, not one of the classmates came up. After over an hour of waiting, the friends had vanished from sight.
Sia was devastated after this. She was inconsolable for her son, who was having a really difficult day on what should have been an enjoyable one.

The New York Post was informed by Teddy’s father, “I was bummed, I was bummed out for sure.”Teddy found it sad that they hadn’t arrived one hour into the celebration because, to him, that was the most important thing. The parents sought to divert their son’s attention with pastimes like arcade games in an effort to lift his spirits.
In an effort to raise awareness that something like this should never happen to anyone, Sia chose to snap a picture of Teddy and post it online. She didn’t anticipate, though, that Teddy’s dejected picture would become so popular and garner so much attention. When she saw how much publicity it garnered, she even regretted posting it.
Teddy received birthday wishes from hundreds of people, many of whom also sent gifts. The Phoenix Suns and the Phoenix Rising MLS team welcomed the family to their forthcoming games as part of their efforts to brighten Teddy’s day a little bit.
Only one parent apologized to Sia on behalf of all the other parents who didn’t bring their kids to the celebration.
Even if this narrative left us feeling let down, it should serve as a reminder to exercise greater consideration and thoughtfulness.
Watch the video below to learn more about the narrative.


Leave a Reply